Copyright © 2015 Powered by MWeb, Theme used GitHub CSS.
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
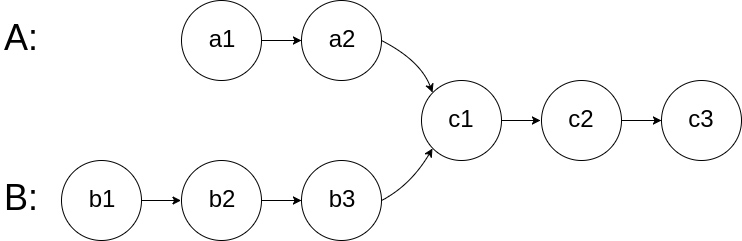
在节点\(c1\)开始相交。
示例 1:

输入: intersectVal = 8, listA = \([4,1,8,4,5]\), listB = \([5,0,1,8,4,5]\), skipA = 2, skipB = 3
**输出:**Reference of the node with value = 8
**输入解释:**相交节点的值为 \(8 \)(注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 \(0\))。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 \([4,1,8,4,5]\),链表 B 为 \([5,0,1,8,4,5]\)。在 A 中,相交节点前有\(2\)个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有\(3\)个节点。
示例 2:

**输入:**intersectVal = 2, listA = \([0,9,1,2,4]\), listB = \([3,2,4]\), skipA = 3, skipB = 1
**输出:**Reference of the node with value = 2
**输入解释:**相交节点的值为 \(2\) (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 \(0\))。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 \([0,9,1,2,4]\),链表 B 为 \([3,2,4]\)。在 A 中,相交节点前有 \(3\) 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 \(1\) 个节点。
示例 3:

**输入:**intersectVal = 0, listA = \([2,6,4]\), listB = \([1,5]\), skipA = 3, skipB = 2
**输出:**null
**输入解释:**从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 \([2,6,4]\),链表 B 为 \([1,5]\)。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
**解释:**这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
注意到这样一个事实,如果两个链表相交,那么在相交节点前面的两个分叉上,正好相差这两个链表长度之差的元素个数。因此,首先遍历两个链表,得到链表长度,然后长度更长的链表先往前走长度之差的步数,然后后面两个链表向前推进到相等即为结果。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
//首先遍历两个链表查询长度
int l1 = 0;
ListNode h1 = headA;
while (h1 != null) {
h1 = h1.next;
l1++;
}
int l2 = 0;
ListNode h2 = headB;
while (h2 != null) {
h2 = h2.next;
l2++;
}
//长度更长的那个需要先走几步,直到两个长度相等时才同时前进。
h1 = headA;
h2 = headB;
int dif = l1-l2;
if (dif > 0) {
while(dif-- >0) {
h1 = h1.next;
}
} else if (dif < 0) {
while(dif++ < 0) {
h2 = h2.next;
}
}
int len = Math.min(l1, l2);
while (h1 != h2){
h1 = h1.next;
h2 = h2.next;
}
return h1;
}
}
Copyright © 2015 Powered by MWeb, Theme used GitHub CSS.